Fast packet I/O
Rohit Kumar
•
19 August 2024
•
1 min
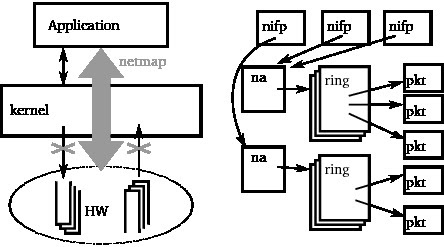
Netmap is a framework for fast packet I/O from userspace.
OS kernel implements TCP/IP stack protocols up to the transport layer. While the applications layer protocols (HTTP, FPT, SSH, SMTP etc) are implemented in userspace. Per packet dynamic memory allocation, system calls overhead and memory allocation make traditional Linux network stack inefficient. Netmap tries to solve this problem make the packet data-path efficient.
Netmap uses these techniques to get it’s high performance
- a lightweight metadata representation, processing of large number of packets in each system call, thus amortizing its cost;
- preallocated, linear, fixed size packet buffers
- removal of data-copy costs by granting applications direct, protected access to the packet buffers of packets between interfaces;
Netmap API
netmap has been implemented as kernel module for FreeBSD and Linux.
ioctl(.., NIOCREG, arg)
The argument contains the interface name, and optionally the indication of which rings
we want to control through this file descriptor.
Other fast packet I/O solutions
XDP(express data path) is an high-performance data-path used to send and receive packets by bypassing os kernel networking stack. It uses e-BPF(extended Berkeley Packet Filter), it is an in-kernel virtual machine, ability to run user-supplied program inside kernel. In short, e-BPF allows us to safely extends the functionalities of kernel without changing the kernel source code or loading kernel module
References
- https://linux-kernel-labs.github.io/refs/heads/master/labs/networking.html#overview
- https://www.cs.cornell.edu/~ragarwal/pubs/network-stack.pdf
- https://github.com/luigirizzo/netmap
- https://ebpf.io/what-is-ebpf/
- https://lwn.net/Articles/740157/