What is LLM ?
Rohit Kumar
•
27 December 2025
•
2 mins
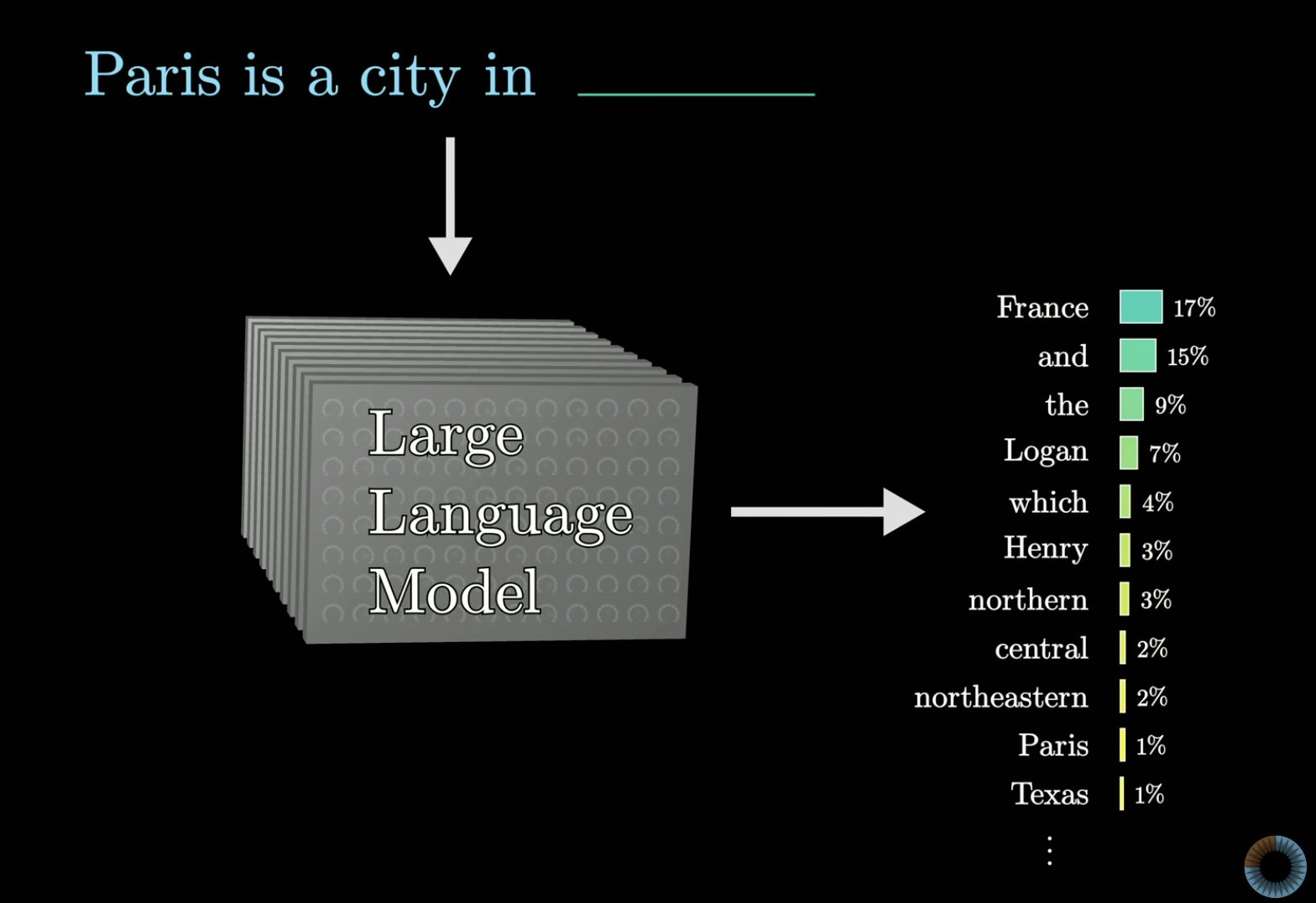
What is LLM: A Beginner’s Guide
LLMs are sophisticated functions that predict the next word (token) in a sequence by assigning probabilities to all possible words.
Key Points:
-
Training: Models learn from enormous amounts of text (GPT-3’s training data would take 2,600+ years to read). They start with random parameters that get refined through billions of examples using backpropagation.
-
Scale: Training requires over 100 million years worth of computation if done sequentially, made possible only by GPUs running operations in parallel.
-
Transformers (introduced by Google in 2017): Unlike older models that processed text sequentially, transformers process all text simultaneously using:
- Attention mechanisms: Allow words to influence each other’s meanings based on context
- Feed-forward networks: Store language patterns learned during training
- Fine-tuning: After pre-training, models undergo “reinforcement learning with human feedback” where workers flag problematic outputs to align the model with user preferences.
How LLM Chatbot Works?
LLM chatbots take a user prompt, encode it into tokens, and generate a reply by repeatedly predicting the next token until a stopping condition is reached.
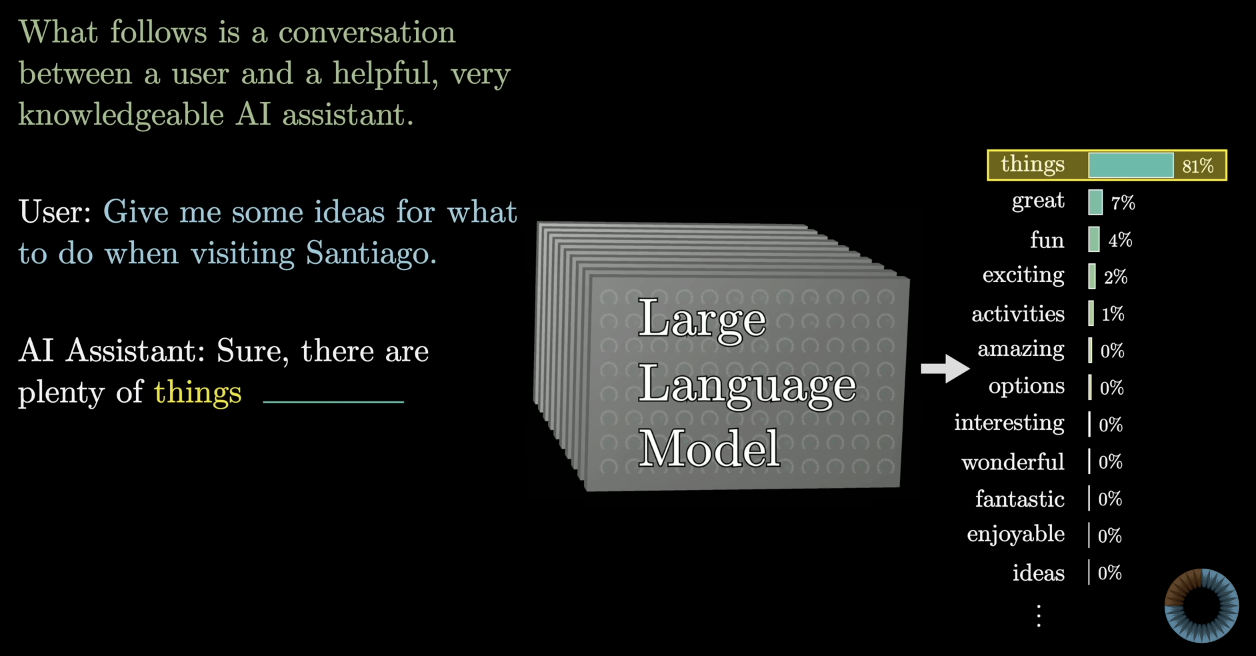
Conversation format
- Prompts are often structured with explicit markers to provide role and intent, e.g.:
User:orQ:for inputAssistant:orA:for the expected response
- Consistent formatting helps the model understand turn-taking and desired output style.
Generation process (high level)
- Tokenization: input text → discrete tokens the model understands.
- Encoding: tokens fed into the transformer to compute contextual representations (attention + feed-forward).
- Decoding: the model predicts the next token autoregressively and appends it, repeating until completion.
- Decoding strategies: greedy, beam search, top-k/top-p sampling, and temperature control how deterministic or diverse outputs are.
Context and transformers
- Attention lets tokens influence each other so responses reflect context from the entire input window.
- During training transformers process tokens in parallel; during autoregressive generation tokens are produced sequentially to preserve coherence.
Augmentation and retrieval
- Retriever-Augmented Generation (RAG) and similar patterns combine an information retrieval step with the LLM:
- Retrieve relevant documents or facts.
- Condition the model on retrieved context to produce more accurate, grounded answers.
- Useful for up-to-date or domain-specific queries the base model didn’t memorize.
Determinism and variability
- The model’s weights are fixed for a given checkpoint, but outputs can vary due to decoding choices (sampling, temperature) and nondeterministic runtime factors.
- Re-running with the same prompt and deterministic decoding yields the same output; sampling introduces deliberate variability.
Training and model behavior
- Model behavior emerges from hundreds of billions of learned parameters refined by gradient-based training (e.g., backpropagation) on large corpora.
- Post-training alignment (fine-tuning, RLHF) adjusts behavior toward safer or more helpful responses.
Practical tips
- Provide clear role markers and concise context.
- Include examples or desired formats in the prompt for consistent output.
- Use retrieval or tool calls for factual, up-to-date, or long-context needs.
- Adjust decoding settings to trade off creativity vs. predictability.